CSS
CSS 스타일 입히기
Cascading : 계단식, 덧칠하기식, HTML태그의 원래 스타일을 Cascading
CSS 속성 : 스타일을 입힐 수있는 가지수 ? 속성수 ?
배경/경계선/폰트/색상/마진-left,top/패딩/박싱/박스라운드-img,color,repeat
대상선별 : 선택자(selector)사용
선택자 기본요소 : id, class , element
- a : <a></a> 태그
- .a : <*class ="a">
- *#a 또는 #a : <*id="a">
- aside.a : <aside class="a">

선택자
- #a{color: green;} : a라는 id를 가지는 엘리먼트에 색상을 적용
- .a{color: green;} : a라는 class에 포함된 엘리먼트에 색상을 적용
- a{color: green;} : a라는 태그를 대상으로 색상을 적용
연산자
- A B : 공백자체가 연산을 의미. A안에 포함된 모든B.
- A>B : A안에 B자식들만 모두선택
- A+B : B의 형제 바로 밑동생
- A~B : A의 동생들 중에 B만 적용
#aa+nav+section : nav의section만 고른것
셀럭터를 이용한 엘리먼트 선택
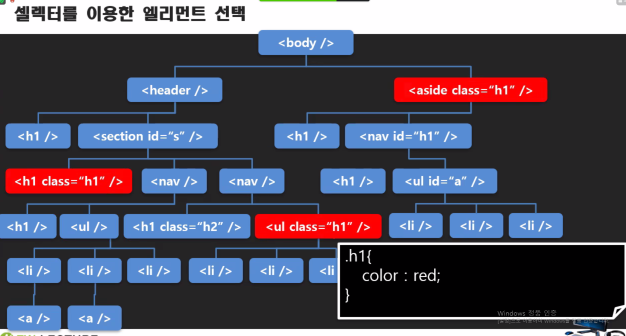
.h1{ color:red; }
class 명이 h1인 태그들을 레드로 적용

aside.h1{ color:red; }
class 명이 h1이면서 aside태그를 가지고있는것 레드로 적용

h1{ color : red; }
h1의 모든태그에 빨간색 적용
*h1{ color ; red; }와 같다.
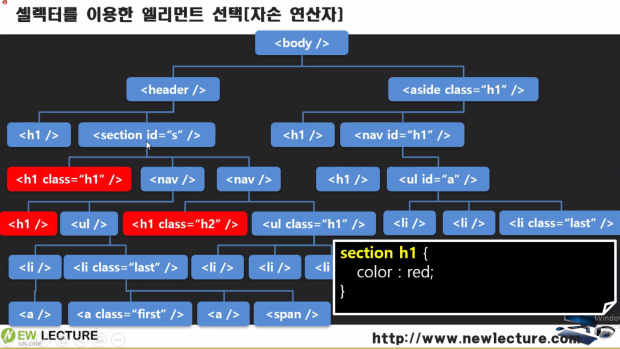
section h1{ color : red; }
section안에 포함된 h1 모두를 찾는다.

section > h1 {color: red; }
section태그의 h1자식만 적용

a.first + span : 바로 밑동생으로서의 span 없음

h1 : 범위가 넓으므로 우선권이없음
.h1 , #h2 범위가 좁혀져 우선권생김
우선순위가 같다면 나중에 적용한게 결과로나온다

h1.h1보다 복합연산자가 더높다
태그명이 속성을 가질땐 우선순위높다

h1{ } :기본 태그이므로 가장 우선순위낮음
.h1{ } : h1클래스로 좁혀짐
h1[lang="ko"] {} : <*lang="ko"> 특정랭귀지속성을 가진 h1태그 , h1에 랭귀지속성 한정사가 한번더 들어가서 우선선위높음
HTML
a[href^="#"]
- ^ 시작 의미
- #으로시작하는것
-
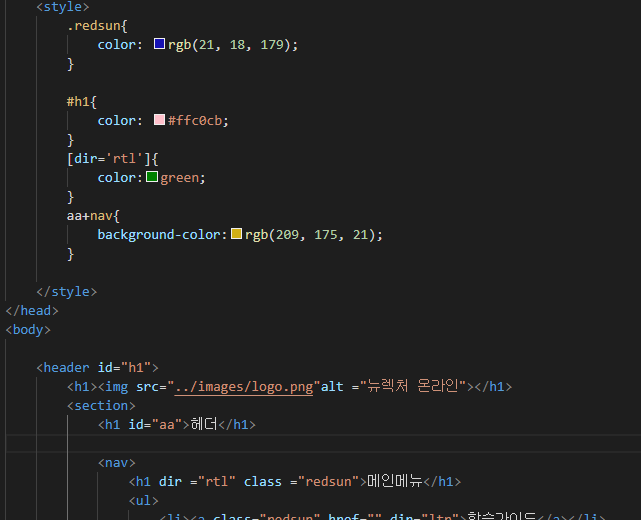
dir
ltr : left to right 왼쪽부터 쓰기
rtl : right to left 오른쪽부터 쓰기
a[dir='rtl']
이 속성에다가도 스타일을 입힐수있다
/* Links with "example" anywhere in the URL */
a[href*="example"] { background-color: silver; }
example이 포함된것들만 비교가능
/* Links with "insensitive" anywhere in the URL,
regardless of capitalization */
a[href*="insensitive" i] { color: cyan;}
i : 대소문자구별하지않겠다
/* Links with "cAsE" anywhere in the URL,
with matching capitalization */
a[href*="cAsE" s] { color: pink;}
s : 대소문자를 가린다.
/* Links that end in ".org" */
a[href$=".org"] { color: red;}
.org로 끝나는것
/* Links that start with "https" and end in ".org" */
a[href^="https"][href$=".org"] { color: green;}
"https" &".org"
두가지속성만족시
연습
- A B : 공백자체가 연산을 의미. A안에 포함된 B의 하위요소. A의 자손만 (B의 자식)

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.aa div{
color : red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="aa">
<p>자식1</p>
<div>
<p>aa의 자손</p>
</div>
<p>자식2</p>
<div>
<p>자손2</p>
<ul>
<li>자손3</li>
<li>자손3</li>
<li>자손3</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- A안에 B자식만 선택

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
section>p{
color : red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="aa">
<p>Child 1</p>
<div>
<p>Descendant1</p>
<section>
<p>Descendant2</p>
<ul>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
</ul>
</section>
</div>
<p>Child 2</p>
<section>
<p>Descendant2</p>
<ul>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
</ul>
</section>
</div>
</body>
</html>- A+B : B의 형제 바로

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div+p{
color : red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="aa">
<p>Child 1</p>
<div>
<p>Descendant1</p>
<section>
<p>Descendant2</p>
<ul>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
</ul>
</section>
</div>
<p>Child 2</p>
<p>Child 3</p>
<section>
<p>Descendant2</p>
<ul>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
<li>Descendant3</li>
</ul>
</section>
</div>
</body>
</html>
'2021 Newlecture > HTML & CSS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| flex / flex-flow / justify-content / (0) | 2021.03.11 |
|---|---|
| 블록태그와 인라인태그 / flex (0) | 2021.03.09 |
| em 과 rem / height : inherit (0) | 2021.03.09 |
| Block 레이아웃 / overflow / 값 할당 단위 (0) | 2021.03.08 |
| Button / Image / pre / CSS 그룹화 , id 적용 (0) | 2021.03.02 |
| Section, 지역화, 블록태그, 인라인태그, 테이블태그 (0) | 2021.02.26 |
| 시멘틱태그 (0) | 2021.02.26 |
| 상대경로와 절대경로 차이 /크롬 확장프로그램/ HTML 문서구조 (0) | 2021.02.23 |